Introduction
In this blog we discuss what is meant by “Design for Reliability”, or “DFR”, we will also look at why is it important and an example process you can follow. Most companies already practice reliability engineering within the design, whether formally or informally. However, implementing a structured reliability programme, such as DFR, can significantly improve your business. This may be through reduced environmental waste; optimized product life cycle costs; improved reputation.
What is Design for Reliability?
Design for Reliability (DFR) is an engineering process that encompasses tools and procedures to ensure that a product meets its reliability requirements. The reliability requirements should be fully defined and include an item’s function, usage conditions, as well as the tolerated level of risk at specific points in time. The DFR process should be implemented throughout the product life cycle from the design stage through to product disposal. Design for Reliability will proactively improve product reliability by seeking to minimize weaknesses in design that lead to early failure. DFR is a process that relies on an array of reliability engineering tools with a focus on using the right tool at the right time in the product life cycle.
Why is Design for Reliability Important?
A well-implemented Design for Reliability process will ensure that customer expectation for reliability is fully met throughout the life of the product with low overall life cycle costs.
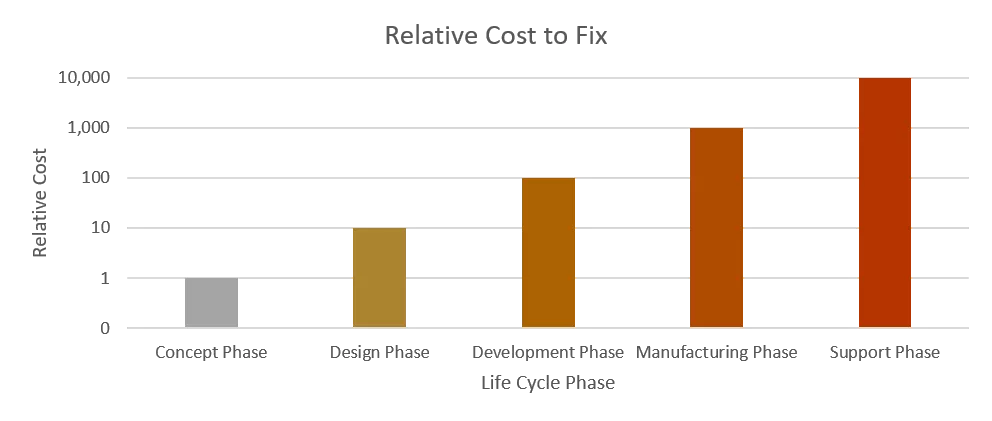
It is advantageous to include reliability activities from an early stage in the design process. It is often said each subsequent stage of the product life cycle, a fix is typically 10 times more expensive. By following a Design for Reliability process, more reliability issues are found earlier on, when they are cheaper to fix. Both provide a saving to the producer and consumer and reduce environmental waste.
The Design for Reliability Process
The Design for Reliability process encompasses a variety of techniques and practices, describing the overall order of deployment that an organisation needs to follow in designing reliability into its products. The scale of the process can vary depending on the size of the company and the cost-benefit analysis of implementing the process.
There are many reliability tools available and their selection should depend on the process requirements and analysis objectives. Remember, the DFR analysis aims to drive improvements – and avoid “analysis paralysis”!
The use of different tools and techniques will vary across the product life cycle and fluctuate with the level of detail of the reliability analysis. The image below shows the typical places for many common reliability tools, practices and techniques.

A good toolkit of techniques available to reliability engineers should enable them to:
- Help ensure product capability;
- Predict product/process failures;
- Understand why failures occur;
- Objectively improve a product/process.
The ReliaSoft suite
We have seen companies implement Design for Reliability programmes with different software tools for each analysis technique. This results in difficulties to build consistent and traceable relationships between the tools. The ReliaSoft DFR Suite is an integrated suite of tools that can help you bring a reliable product to market using a DFR process focused on:
- Designing out or mitigating potential failure modes before production release;
- Based on an understanding of the physics of failure;
- Testing to discover issues and statistical analysis methods for reliability prediction.
Summary
In this article we have introduced the topic of Design for Reliability, explained why it is important, and the benefits of implementing such a process. We also showed a typical example DFR process which you can start to use. DFR can open up many opportunities for companies who want to move beyond securing a basic offering to the marketplace to creating a true competitive advantage in which reliability plays a critical role in customer satisfaction.







